The report “COVID-19 Impact on Composites Market by Fiber Type (Glass Fiber, Carbon Fiber and Natural Fiber), Resin (Thermoset Resin and Thermoplastic Resin), End-use Industry and Region – Global Forecast to 2021”, by MarketsandMarkets.
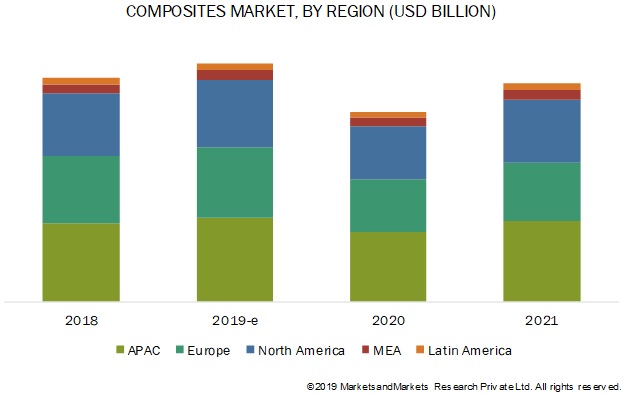
The global composites market size is expected to decline from 90.6 billion in 2019 to USD 82.9 billion by 2021, at a negative growth rate of 4.4% over 2019. The composites industry is expected to decline in 2019 due to supply chain disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.

The automotive and transportation industry
The saving in weight for a given level of strength makes the use of composites vital in the automotive and transportation industry. The automotive and rail sectors are focused on reducing weight and increasing the efficiency of vehicles and exploiting more advanced materials. Due to COVID-19, automobile manufacturers across the globe are facing severe impact. The US, Japan, South Korea, Italy, Germany, and the UK are the most affected countries, which are the major automotive and transportation manufacturing countries. The majority of the automobile manufacturers will witness a direct impact of the pandemic situation on their 2020 revenue.
The glass fiber composites market
The glass fiber composites have superior attributes, such as strength, flexibility, durability, stability, lightweight, and resistance to heat, temperature, and moisture. Glass fiber composites are used in different end-use industry segments, such as construction, wind, pipe and tanks, marine, and transportation. There is a high demand for glass fiber composites from the wind energy and construction and infrastructure industries. It is expected to decline due to lockdown resulting in reduced wind capacity installations and the temporary suspension of operations in the automotive, aerospace, and construction industries.
The thermoset composites market
In thermoset composites, thermoset resin is used as a matrix with fibers, including glass fiber, carbon fiber, natural fiber, and others. Currently, thermoset resins are widely used for manufacturing composites, as when uncured, they are in a liquid state at room temperatures. This unique property of thermoset resin allows for the convenient impregnation of reinforcing fiber. But, because of the lockdown situation occurred due to COVID-19, many floor workers are unable to work in manufacturing facilities, which has resulted in the reduction in output of several resins, such as epoxy resins. Thus, the demand for thermoset resins is expected to decline during the forecast period.
The aerospace and defense end-use industry
The aerospace industry is a major consumer of composites. Growing environmental concerns and search for high strength light-weighting material to increase fuel efficiency have put composites in the limelight in the aerospace and defense industry. The COVID-19 pandemic has pushed the global aerospace and defense industry into an unprecedented crisis. A deep downfall in revenue and cash flow seems imminent for most airlines as well as OEMs and their suppliers in the aircraft production ecosystem. This huge impact on material suppliers would mainly hit the composite demand in aircraft manufacturing.
Read the report here.












