ECOXY is a 4-year Large Scale Collaborative Project coordinated by CIDETEC, an organization for applied research that integrates three international reference institutes in the fields of energy storage, surface engineering and nanomedicine.
ECOXY Project will develop innovative bio-based epoxy resins and fibre-reinforcements by targeting advanced functionalities. This project has received funding from the BioBased Industries Joint Undertaking under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (call BBI 2016.R7).
The state of art
Fibre-reinforced thermoset composites (FRTCs) are attractive materials for high demanding sectors, such as automotive or construction, due to their lightweight and excellent mechanical properties. However, the lack of reprocessability and difficulty for repairing and recycling significantly increases the overall material cost and causes grave environmental concerns. Additionally, the vast majority of polymer matrices and fibres used in their manufacturing are non-renewable fossil-derived materials or require high amounts of energy for their production.
The project
Aiming at addressing those limitations by involving the European bio-based industry, ECOXY will develop innovative bio-based epoxy resins and fibre-reinforcements to produce new sustainable and techno-economically competitive fibre-reinforced thermoset composites (FRTCs) by targeting advanced functionalities: reparability, reprocessability and recyclability (3R). The 3R functionalities will be achieved by using new resin formulations where commonly used curing agents will be replaced by dynamic hardeners. These new formulations, under certain operational conditions, make it possible to obtain materials that are:
- repairable: delamination and matrix micro-cracks will be repairable by applying heat and pressure.
- reprocessable: cured laminates can be reprocessed to create new 3D parts (impossible with traditional FRTCs).
- recyclable: via mechanical and chemical (at a lab scale) recycling. End-of-life parts & production scraps will be recovered for the production of short-fibre reinforced parts.
- bio-based: in sharp contrast to new type of polymer networks that have emerged in recent years, which can inherently be 3R but are still based on non-renewable fossil-derived materials, ECOXY will develop bio-based resin and fibre-reinforcement materials to produce bio-based 3R FRTCs.
These will be achieved by developing:
- tailor-made bio-based epoxy monomers (including biorefinery products)
- upgraded and functional bio-based fibres (natural and PLA)
- specific formulations for FRTCs manufacturing processes (RTM, wet compression moulding and pultrusion)
- additional functionalities such as flame-retardancy for 3R resin and self-healing for fibres.
The selected prototypes will be validated for automotive and construction sectors using relevant standards and applicable certifications.
Partnership
ECOXY is supported by 13 partners from 8 different European countries (Belgium, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Poland, Spain and The Netherlands) in order to meet the marked objectives. The consortium is well balanced: 6 partners are SMEs, 6 partners are research institutions, and there is also 1 academia from different sectors necessary to complete the value chain of the project: CENTEXBEL, Weverij Flipts & Dobbels Nv and Avantium will work in the development of bio-based fibres. CIDETEC, University of Nice Sophia Antipolis and Specific Polymers will develop the bio-based 3R thermoset and FRTCs. Fraunhofer ICT, Fundacion AITIIP, AIMPLAS, Centro Ricerche Fiat and Bergamo Tecnologie will deal with the fabrication and validation of composite parts. European Composite Recycling Technology will be leader of work package dealing with recycling, repairing and reprocessing and Vertech Group will be the one doing the economic and environmental assessment.
First bio-based epoxy result
The last December, the research team announced that within the framework of the ECOXY Project, biofibres and bio-based resins are being developed to substitute current resins. Due to dynamic hardeners of these bioresins the covalent crosslinks can change under temperature and pressure. This behaviour allows to form, weld or recycle the manufactured composites at the end of their lifetime.
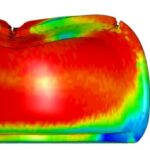
Composites out of these bio-based resins and bio-based flax fibres have been successfully processed using the wet compression moulding process, that was monitored with a dielectric in-mould sensor to optimize the curing conditions. The process for processing the new materials was optimised on the basis of mould filling studies to achieve a complete infiltration of the fabrics. The production was demonstrated on a rear seat back panel, which is used in automobiles.
 Information about ECOXY Project
Information about ECOXY Project
– Total budget: 4.85 M€
– Duration: 01/06/2017 – 30/11/2020
– Web: www.ecoxy.eu
Source: CIDETEC, ECOXY Project