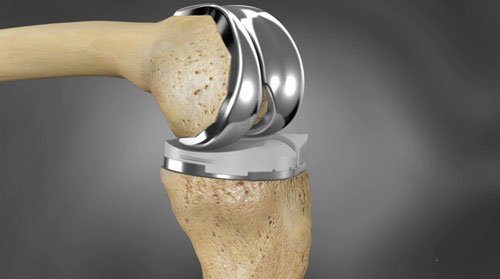
Various scientific projects performed at the Research Center for Advanced Materials (Cimav), Unit Monterrey, in the north of Mexico, aimed at one goal: conducting research and apply the knowledge in the development of biomedical implants, since the ones existing in the domestic market come generally from foreign manufacture.
Currently this center, part of the National Council for Science and Technology (CONACYT) and located at the Park of Research and Technological Innovation (PIIT), works on the study of novel materials, coating systems and specific properties to use in the manufacture of hip and knee implants, and, in the future, of dental parts.
It is the combination of research focused on nanostructured materials with biocompatible and antibacterial properties. In this regard, Ana Maria Arizmendi Morquecho, Cimav scholar, explains that the challenge is to find appropriate measures to improve the compatibility of a metal structure with the chemical composition of bone tissue and human bone’s nanostructures.
“The biocompatibility is the ability of a material to be in contact with a living being without adverse effects, therefore represents one of the most important properties in the manufacture of a biomedical implant. Currently the knee and hip implants are complex systems made of titanium alloy substrates, which require a coating compatible with bone tissue and physiological fluids using nanotechnology; to achieve this intermediate coating deposition techniques of new synthesized materials are used.
“We use a ceramic material which is compatible with the bone, in this case hydroxyapatite, which is used as a matrix and nanoparticles from other materials are used to reinforce it and provide improvements to the bicompatibility, joint wear and mechanical properties”, explains Arizmendi Morquecho.
She reiterates that the materials are increasingly complex and functional, since it is needed of them to be resistant to wear, having improved mechanical properties and may be compatible with the human body simultaneously, in addition to abide to public health requirements.
The researcher at Cimav explains that due to the complexity of the system for the knee implant, scientific work is completed in parts: research is focused on the coating that will join the the metal substrate (titanium alloy) to the bone, the study of polymeric biomaterials which will be in contact with the articulation and both focused with the entire system compatibility with body fluids.
“Each research is a graduate level thesis and participation of a multidisciplinary group of researchers that ultimately come together for the same product, a final component. The next stage of the project is to validate in vitro and in vivo synthesized material at a laboratory level, for which the link with other entities such as medical schools and academic institutions specialized in this type of testing is necessary. It’s important to note that compatibility tests are standardized under sanitary policies and those entities are responsible for validation in our developments.”
The materials specialist refers that the aforementioned research has led to ten scientific papers published in scientific journals.
To get to the finished product, Cimav has vinculated with higher education institutions and other technology research centers, but still needs to find domestic companies interested in manufacturing the final component.
In this regard, Arizmendi Morquecho notes that the advantage of working in the PIIT is the ease of linking with other institutions nationally and globally that have other technologies, additional infrastructure and can be useful for obtaining the final product.
“The science-technology-innovation ecosystem is a necessity in the region, so the creation of the PIIT is a path we must take to move faster. Doing research is not everything, business participation is required and the participation of a governmental entity to offer innovative and necessary products for the national population. Everything has to do with the momentum of the innovation ecosystem in the state,” she concludes.
Source: Investigación y Desarrollo