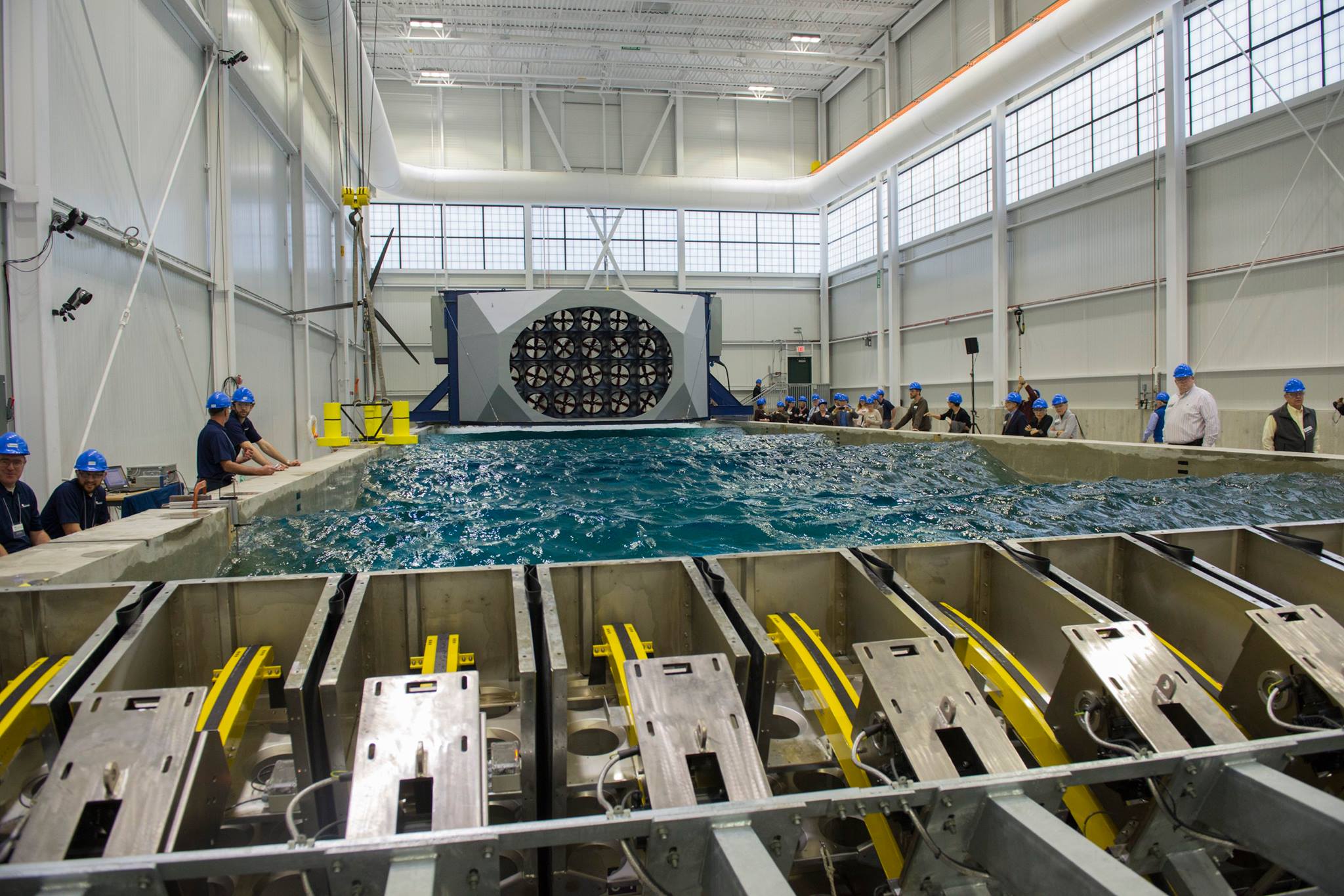
The University of Maine unveiled a $13.8 million laboratory that will allow companies to test designs for offshore wind turbines, underwater turbines and ships against the toughest ocean conditions.
“These will be the only test facilities of their kind in Maine with world-class capabilities to educate students and conduct cutting-edge research and development,” said Habib Dagher, director of the Advanced Structures and Composites Center on campus. “The research and development will support the growth of the ocean economies and shipbuilding sectors in Maine and the nation.”
The lab features a 16-foot-deep wave pool with a rotating wind machine. It’s meant to test 1:50 scale models against waves up to 2½ feet, or 125 feet when scaled up, and the scale equivalent of hurricane-force winds.
At one end of the pool, 16 large “paddles” push the water to create the waves of varying sizes and frequencies to see how models hold up to the rarest and most severe storm conditions.
During the ceremony, Gregory Powell, chairman of the Harold Alfond Foundation, handed the center a check for $3.9 million, joining the nearly $10 million already raised to build the new lab.
In recognition of that award, the university named the new center the Harold Alfond W2 Ocean Engineering Laboratory and Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory, which will be part of the existing Advanced Structures and Composites Center.
Additional funding came from the U.S. Economic Development Administration, National Science Foundation, Maine Technology Institute and a $5 million voter-approved bond.
Dagher said the laboratory would offer its services to energy companies, shipbuilders and others who want to test small-scale designs to determine, at a lower cost, how well the full-scale versions would perform in rough seas.
For example, if a shipbuilder wanted to test a model, it could send the design schematics to the composites center, which would print the model on a 3-D printer. That model could be ready for testing in the pool the next week. In that pool, it could face off against wave conditions so severe that they’re only seen once a century in a given section of ocean.
Another research facility attached to the W2 laboratory is expected to open in the summer of 2016. That lab will feature robotics and other equipment to study and develop thermoplastic composites. Composites center officials say they expect to start installing equipment in that facility in the coming weeks.
Since the university opened a Wood Composites Center in 1996, it has expanded to study other types of structures and materials, eventually rebranding as the Advanced Structures and Composites Center.
More than 1,800 graduate and undergraduate students have worked and researched there since.
U.S. Sens. Susan Collins and Angus King, U.S. Rep Bruce Poliquin, and business, engineering and university leaders from across the state attended Monday’s event. Officials representing the U.S. Economic Development Administration, the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy and other federal agencies also joined the more than 250 attendees.
“Maine is a maritime state,” Collins said. “The ocean is our heritage, and it is our future.”